CHINA DIRECTIONAL DRILLING WHIPSTOCK SIDETRACKING SYSTEM
To reduce drilling costs, the whipstock is used to mill the casing and sidetrack a new wellbore. The sidetracking tool primarily comprises the whipstock and casing window milling components.
Tel: + 86 05386368027
To reduce drilling costs, the whipstock is used to mill the casing and sidetrack a new wellbore. The sidetracking tool primarily comprises the whipstock and casing window milling components.
Our company's hydraulic whipstocks feature ground spear and hydraulic anchoring types. The hydraulic anchoring ensures precise azimuth alignment and secure anchoring. This tool is essential when the casing in the oil layer is significantly damaged or buried in sand due to collapse, making the oil well non-productive. To reduce drilling costs, the whipstock is used to mill the casing and sidetrack a new wellbore. The sidetracking tool primarily comprises the whipstock and casing window milling components.
1. Cambered whipstock
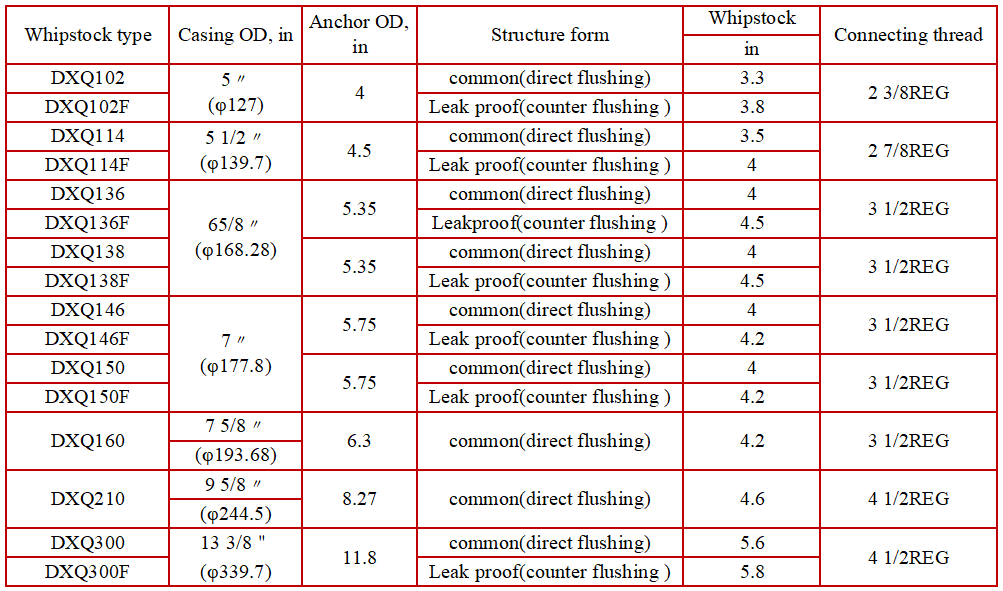
The cambered whipstock features an arc-shaped incline and undergoes a super-hardening treatment, resulting in a high degree of anastomosis with the cone mill bit. This design provides excellent centralizing effects, custom window openings, smooth operation, and precise azimuth control. During construction, it facilitates easy pressure control, reduces drilling suppression and jumping, and minimizes the risk of downhole accidents.
With advancements in directional and horizontal well technology, multilateral wells have garnered increasing attention as an extension of directional well technology. The retrievable whipstock is a crucial tool for multilateral well drilling, playing a vital role in both drilling and completion.
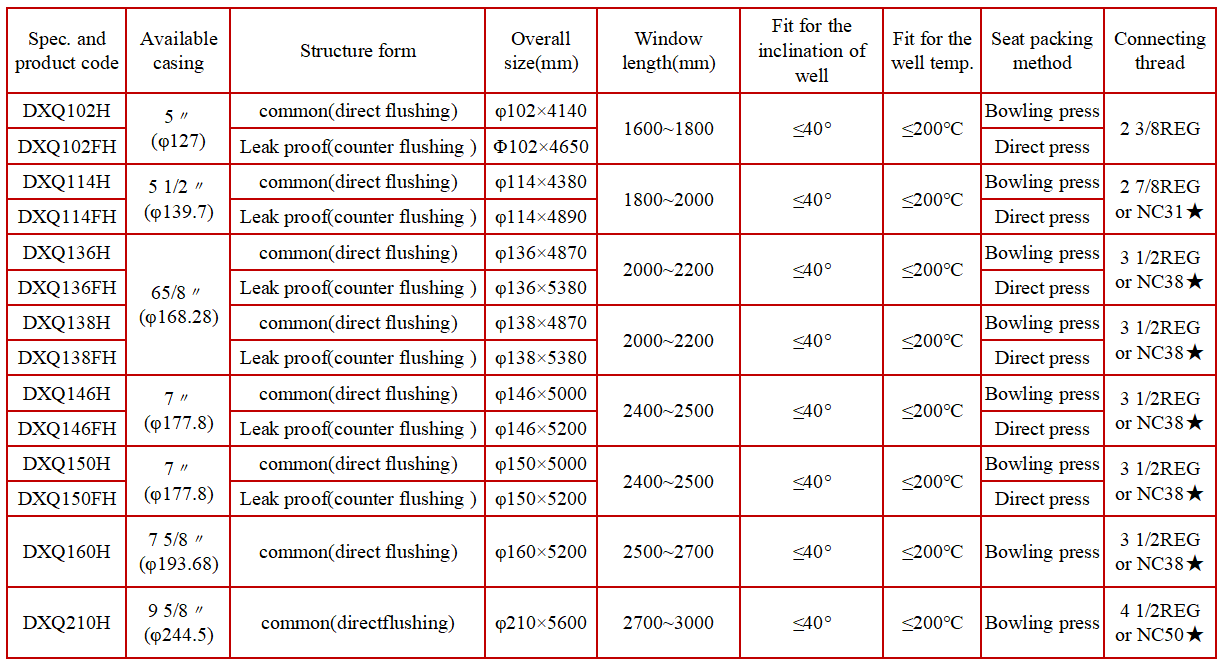
Our company's retrievable whipstock is designed for ease of operation, reliable seat sealing, high recovery success rates, and reusability. It comprises three main components: the whipstock, a circulating well flush valve, and a fishing tool.
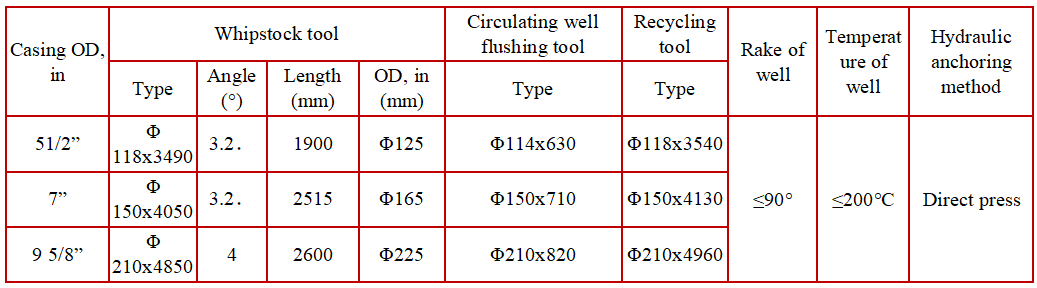
To better meet the needs of double casing or sidetracking operations on extended sections, our company has developed the two-cylinder whipstock. This product addresses the challenges of long cycles and difficult construction. It features a dual hydraulic cylinder structure with four groups of slips and a special internal connection that ensures liquid sealing and pressure flow. The two hydraulic cylinders operate independently, while the four groups of slips provide secure and accurate directional anchoring, ensuring a safe and reliable closure process during construction.

Usage:
1. Well Cleaning:
- Select specifications according to design requirements. Ensure the diameter and length meet or exceed gauge specifications. Avoid jamming during the process.
2.Scraping Pipe:
- Use a spring-type scraper, scrubbing 5 times at 5m above and below the sealing point to clean and smooth the well wall.
3. Guide Screw Check:
- Ensure all guide screws are tightened properly.
4. Mud Pump and Ground Manifold Check:
- Inspect to confirm no puncture leakage when the seal is set at 25 MPa.
5. Lowering the Guide:
- Attach the guide to the pipe string's lowest end as per design. Lower it to the predetermined position and connect the upper drill pipe.
6. Well Washing:
- Wash the well thoroughly according to product model and method until it is clean and free of debris.
7. Sealing:
- Remove the lower drill pipe, insert a steel ball (for backwashing, the ball is inside the product). Connect the upper drill pipe, check the depth, adjust the tool surface, record the hanging weight, and pressurize the seat seal in a positive cycle. Pressurize 3 times at 22-25 MPa each.
8. Pressure Test:
- After 3 pressure tests, perform a downward pressure test:
- DXQ102~DXQ138: Press down 5~6 tons
- DXQ150~DXQ160: Press down 7~8 tons
- DXQ210/DXQ300: Press down 10~12 tons
- Lift the tool 3~4 tons. If no relative movement of the pipe string to the wellhead, the seat seal is firm.
9. Release:
- After the pressure test, lift the pipe string to the hanging weight before the seat seal. Rotate the drill string forward for more than 30 circles, then lift the pipe string to pull out the release short section.
Precautions:
1. Drill Pipe Clearance:
- Clear the inner hole of the drill pipe before lowering the guide to prevent debris clogging.
2. Uniform Speed Lowering:
- Lower the guide uniformly and smoothly. Avoid violent lifting and releasing, especially in backwashing wells.
3. Thorough Well Washing:
- Wash the well thoroughly according to product specifications until the outlet is clean and free of debris.
4.Use of Clean Water:
- Use clean water for the guide seat seal.
5. No Lifting After Lowering:
- Once the guide is lowered into the well, it should not be lifted out.